Astra Missile Tested Successfully
 |
 |
India on 21 December 2012 test launched its indigenously developed beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air interceptor missile Astra at the interim
test range (ITR) at Chandipur in Odisha.
The missile was fired from the launch pad number two of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) run missile testing centre at around
13.30 hours to confirm its reconfigured propulsion, control and guidance systems.
The launch was carried out against an electronic target and it destroyed its target - a small pilotless Lakshya aircraft - which was launched from the
same base just minutes before the firing of the missile.Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) scientists said Friday’s trial was
only a rehearsal.
The missile would be test-fired again on Saturday with an actual seeker to intercept Lakshya. In Friday’s mission, Astra was guided towards the electronic target in a ground-to-air launch.The altitude of engagement was 4 km and all the parameters were validated, the scientists said.The missile was also tested for midcourse guidance against an electronic target.
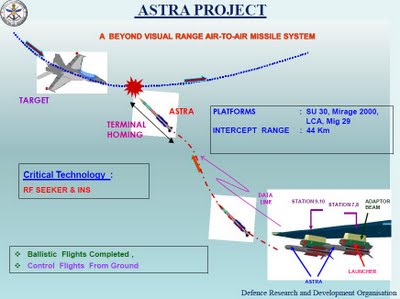
ASTRA
The Astra, built by the Defence R&D Laboratory (DRDL), Hyderabad, will allow IAF pilots to hit enemy aircraft up to 44 km away, at altitudes up to 20,000 metres. Improving on that will be the Astra Mk II, with a longer range of 80 km. ASTRA is a Beyond Visual Range (BVR) air to air missile indigenously designed and developed to engage and destroy highly maneuvering supersonic aerial targets. This highly agile and accurate missile can intercept high speed, highly maneuvering targets and can pull High level maneuvers. The kill boundary of this vehicle gives the enemy no chance of survival. This is one of its class with a low all up weight to have high launch range capability, this weapon system is meant for platforms like SU 30MKI, Mirage 2000 of Indian Air force and LCA developed by DRDO.
The Astra incorporates many cutting-edge technologies. Here is how an Astra would take on an enemy fighter: an IAF fighter’s radar picks up
the target; the pilot launches an Astra missile. A high-energy propellant quickly boosts the missile to several times the speed of sound. At ranges
beyond 15 km, the Astra cannot “see” its target, so the IAF fighter guides the missile, relaying the target’s continually changing
position over a secure radio link. Once it is 15 km from the target, the Astra’s onboard seeker picks up the target; after that the Astra homes
in on its own.
At this point, the target would start turning and diving to throw off the missile. But the Astra manoeuvres better, and moves much faster, than even
the most agile fighters. A radio proximity fuse measures the distance to the target. When the target is within 5 metres, the Astra’s radio
proximity fuse detonates its warhead, sending a volley of shrapnel ripping through the enemy fighter.
Salient Features
Airborne Launcher adaptable to Different Fighter Aircrafts
Smokeless Propulsion
Inertial Mid-Course & Terminal Homing
State-of-art ECCM features
All weather capability
Launch Speed 0.4M to 2M
Launch Altitude SL to 20Km
Launch Range 80Km
