India's Most Advanced Missile Agni IV Launched Successfully
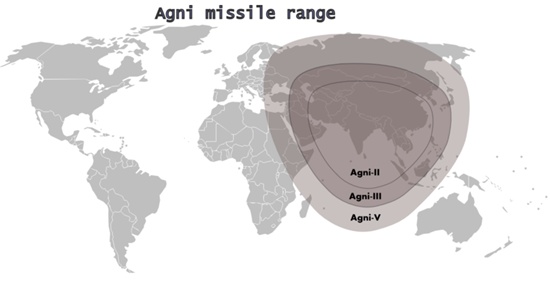 |
| Range of Agni Missiles |
| Video Showing Missile Launch |
India today successfully test fired the most advanced long range missile system Agni-4 today(15th november,2011). The missile was launched from a Road Mobile System at 9.00 AM from Wheelers’ Island off the coast of Odisha. The missile followed its trajectory with a range of more than 3000 Kms, in a text book fashion, attained a height of about 900 kms and reached the pre-designated target in the international waters of Bay of Bengal. All mission objectives were fully met. All the systems functioned perfectly till the end encountering the re-entry temperatures of more than 3000⁰C.
This missile is one of its kinds, proving many new technologies for the first time, and represents a quantum leap in terms of missile technology. The Missile is lighter in weight and has two stages of Solid Propulsion and a Payload with Re-entry heat shield. The Composite Rocket Motor which has been used for the first time has given excellent performance. The Missile System is equipped with modern and compact Avionics with Redundancy to provide high level of reliability. The indigenous Ring Laser Gyros based high accuracy INS (RINS) and Micro Navigation System (MINGS) complementing each other in redundant mode have been successfully flown in guidance mode for the first time. The high performance onboard computer with distributed Avionics architecture, high speed reliable communication bus and a full Digital Control System have controlled and guided the Missile to the target. The Missile reached the target with very high level of accuracy. Radars and electro-optical systems along the Coast of Odisha have tracked and monitored all the parameters of the Missile. Two Indian Naval ships located near the target witnessed the final event.
Defence Minister Shri A.K. Antony congratulated the DRDO team on its achievement. Dr Vijay Kumar Saraswat, Scientific Advisor to Raksha Mantri, Secretary, Department of Defence R&D and Director General DRDO, who witnessed the launch, congratulated all the Scientists and employees of DRDO and the Armed Forces for the successful launch of AGNI-4. Sri Avinash Chander, Chief Controller (Missiles & Strategic Systems), DRDO and Programme Director, AGNI, while addressing the Scientists after the launch, called it as a new era in the modern Long Range Navigation System in India. He said, “this test has paved the way ahead for the success of AGNI-5 Mission, which will be launched shortly”.
Smt. Tessy Thomas, Project Director AGNI-4 and her team prepared and integrated the Missile System and launched the Missile successfully. In a jubilant tone she said that the DRDO has produced and proven many new state of the art technologies in the Missile System like Composite Rocket Motors, very high accuracy Ring Laser Gyro based Inertial Navigation System, Micro Navigation System, Digital Controller System and very powerful onboard computer system. The Missile, having capability to carry Strategic Warheads for the Forces, has provided a fantastic deterrence to the country and it will be produced in numbers and delivered to the Armed Forces as early as possible.
<<<<< Updates>>>>
Early entry of Agni IV in to Arsenal
A day after the successful launch of the Defence R&D Organisation’s all-new Agni-4 ballistic missile, a triumphant DRDO chief proclaimed it as good as America’s Pershing-II missiles; and declared that India’s missile arsenal could no longer be constrained by technology denial sanctions.
Highlighting the capability of the Agni-4, V K Saraswat, DRDO head, told the media here that this 20-tonne missile could deliver a one-tonne warhead to a distance of 3,500 km, significantly further than the 3,000 kilometres range of the much heavier, 48-tonne Agni-3 missile. Saraswat listed the multiple technological breakthroughs that had permitted this feat — composite rocket motors; a state-of-the-art navigation system and control systems that were both lighter and better.
The DRDO plans to quickly bring the Agni-4 into military service. “We hope to complete the test phase (two launches) in 2012; the user phase (two launches) in 2013; and in 2014 we would offer it for service. We have dramatically shortened the time from development to service,” said the DRDO’s missile controller, Avinash Chander.
DRDO to test Agni-V ICBM in next three months
 Senior defence scientists said Wednesday(16th November) that the near-ICBM Agni-V,
with a strike range of 5,000-km, would be tested sometime in the December-February period.
Senior defence scientists said Wednesday(16th November) that the near-ICBM Agni-V,
with a strike range of 5,000-km, would be tested sometime in the December-February period.
"The three-stage Agni-V is undergoing integration at the moment...it's on schedule," DRDO chief Dr VK Saraswat said, adding that both Agni-IV and V were comparable to the best missiles in their class as far as the technology was concerned.
According to Agni programme director, Avinash Chander, the Agni-V would certainly be ready for induction into the armed forces by 2014.
The 20-tonne Agni-IV and 50-tonne Agni-V are expected to add the required muscle to India's nuclear deterrence posture against China, which has a huge nuclear and missile arsenal like the 11,200-km Dong Feng-31A ICBM capable of hitting any Indian city.
The Agni-IV and V are expected to provide India the required operational flexibility against China as they are endowed with greater accuracy,
fast-reaction capability and road mobility.
Both the missiles will be capable of striking high-value targets deep inside China.
The Agni-V is a three stage solid fuel missile with composite motor casing in the third stage. Two stages of this missile will be made of composite material. Advanced technologies like ring laser gyroscope and accelerometer will also be used in the new missile, allof which were tesed with the Agni-IV.
The Agni-5 is specially tailored for road-mobility, according to Avinash Chander.
The DRDO is successfully developed the canister for these missiles and all India's future land-based strategic missiles will be canisterised.
Made of maraging steel, a canister must provide a hermitically sealed atmosphere that preserves the missile for years. During firing, the canister must absorb enormous stresses when a thrust of 300 to 400 tonnes is generated to eject the 50-tonne missile.
More about India's Integrated Missile Development Program - Click here
